Understanding Income Gaps Across Economically Advanced Nations
Income Inequality by Gini Coefficient – Developed Countries as of 2022
The Gini coefficient is a widely used measure of income inequality, reflecting how evenly income is distributed within a country. This dashboard presents Gini scores for developed countries as of 2022, offering insight into how income gaps vary from one nation to another. Explore how economic policies, labor markets, and social programs affect inequality. Understanding these patterns helps spark conversations around fairness, opportunity, and what it takes to build societies where prosperity is more evenly shared.
The Gini coefficient measures income inequality on a scale from 0 (perfect equality) to 1 (maximum inequality). Higher values indicate greater income disparity.
Conclusion
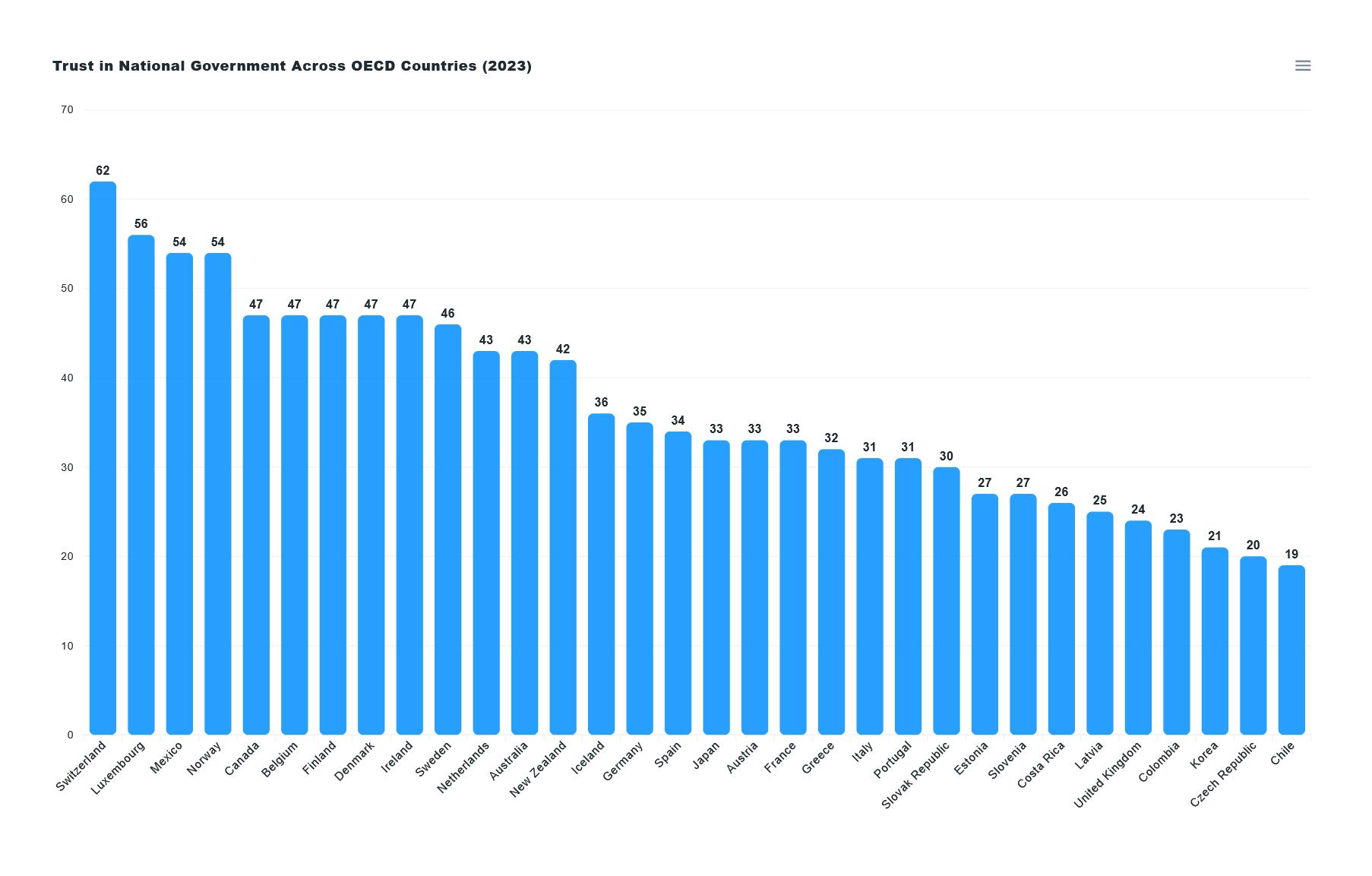
The success of the Nordic countries in achieving high social well-being metrics, despite their challenging climates and high tax rates, can be attributed to the strategic use of tax revenue to fund robust social policies. These policies, including a strong social safety net, work-life balance, equality, and high-quality public services, create an environment where citizens thrive.
This comprehensive approach not only elevates the standard of living but also fosters a sense of community and trust, further enhancing the well-being of these societies. As a result, the need for emigration from these regions has decreased, reflecting the stability and quality of life that their social systems provide.